What Is Wi-Fi?
- What Is Wi-Fi?
- The Complete Beginner's Guide to Wireless Networking
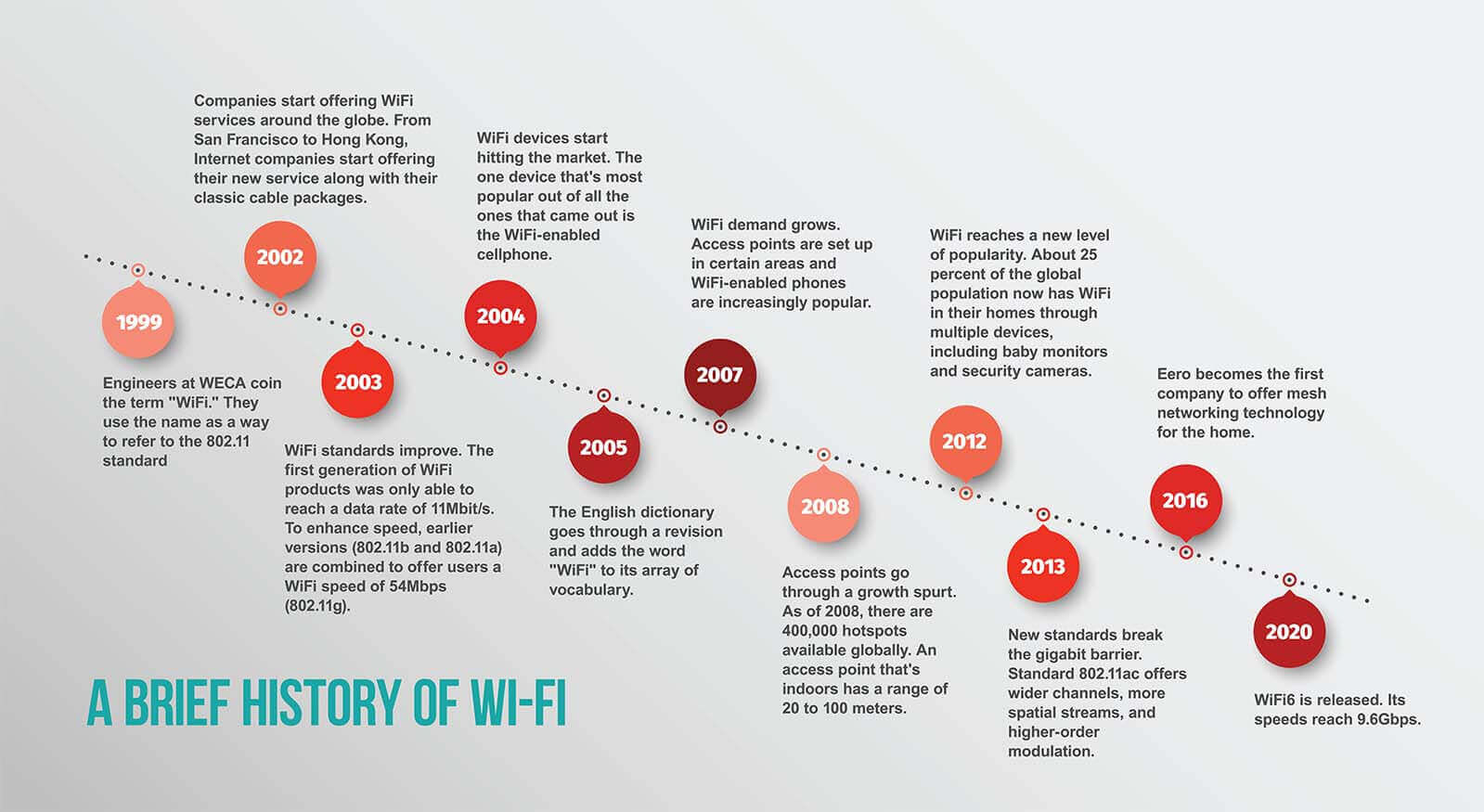
- 1. History of Wi-Fi
- 2. Early Days of Wi-Fi
- 3. Wi-Fi gets standardized
- 4. Wi-Fi Goes Mainstream
- A New Era of Connectivity
- 5. Wi-Fi in Home
- 6. Wi-Fi in Enterprise and Industry
- 7. How Wi-Fi Devices Are Made: The Complete Wi-Fi Technology Life Cycle
- 8. Why Is Wi-Fi So Successful?
- 9. The Generations of Wi-Fi
- Wi-Fi Generations Comparison Table
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wi-Fi
The Complete Beginner's Guide to Wireless Networking
Wi-Fi connects the world---powering everything from smartphones to smart homes, businesses to stadiums, and even industrial robots. But what exactly is Wi-Fi? How did it start, and why is it everywhere? In this article, we break down the story and science of Wi-Fi in simple terms, understand and make the most of their wireless world.
1. History of Wi-Fi
Earlier computer networking was mostly done with cables---wired networking has been around for over 3 decades before Wi-Fi came in! In the 1980s, the idea of using radio waves (wireless) for networking began to take shape.
Wi-Fi may feel like magic, but it's actually built on decades of wireless research.
-
Early Days: In 1985, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the US opened up parts of the radio frequency spectrum for "unlicensed" use (915 MHz, the 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz bands). This meant anyone could use those frequencies (with some rules), without needing to buy an expensive license.
-
First Devices: Cordless phones, baby monitors, and garage door openers used these frequencies long before the first Wi-Fi routers.
-
Birth of Wi-Fi: In the late 1990s, the IEEE introduced the 802.11 standard. Soon after, companies like Apple brought wireless internet to the mainstream---remember the iBook demo where Steve Jobs walked across the stage, surfing wirelessly for the first time?
2. Early Days of Wi-Fi
At first, these new wireless frequencies weren't used for internet. Devices like microwave ovens, baby monitors, cordless phones, and garage door openers started using them.
But soon, companies saw the potential to connect computers without wires. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, the first wireless routers were developed---before there was any universal standard.

So How Does Wi-Fi Work? Wireless Networking Explained Simply
At its core, Wi-Fi is just a way to send data through the air using radio waves---like invisible "data highways" that link your device to the internet.
Basic Flow:
-
Your device (phone, laptop, TV) sends a signal to a Wi-Fi router.
-
The router connects to the internet---usually through a cable or fiber connection.
-
Data travels back and forth between your device and the router using radio waves.
3. Wi-Fi gets standardized
A huge step forward came in the late 1990s, when the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) published the first Wi-Fi standard: IEEE 802.11. This was like giving everyone a common language to build wireless networks.
4. Wi-Fi Goes Mainstream
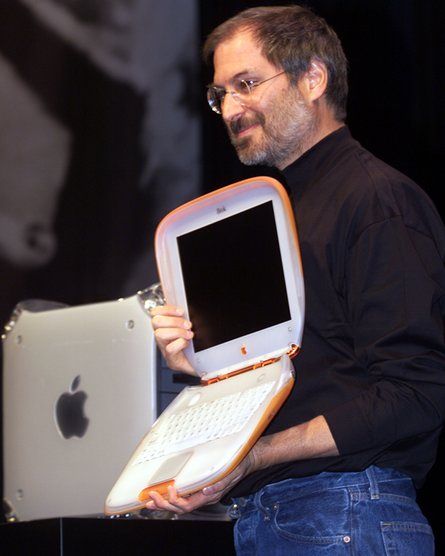

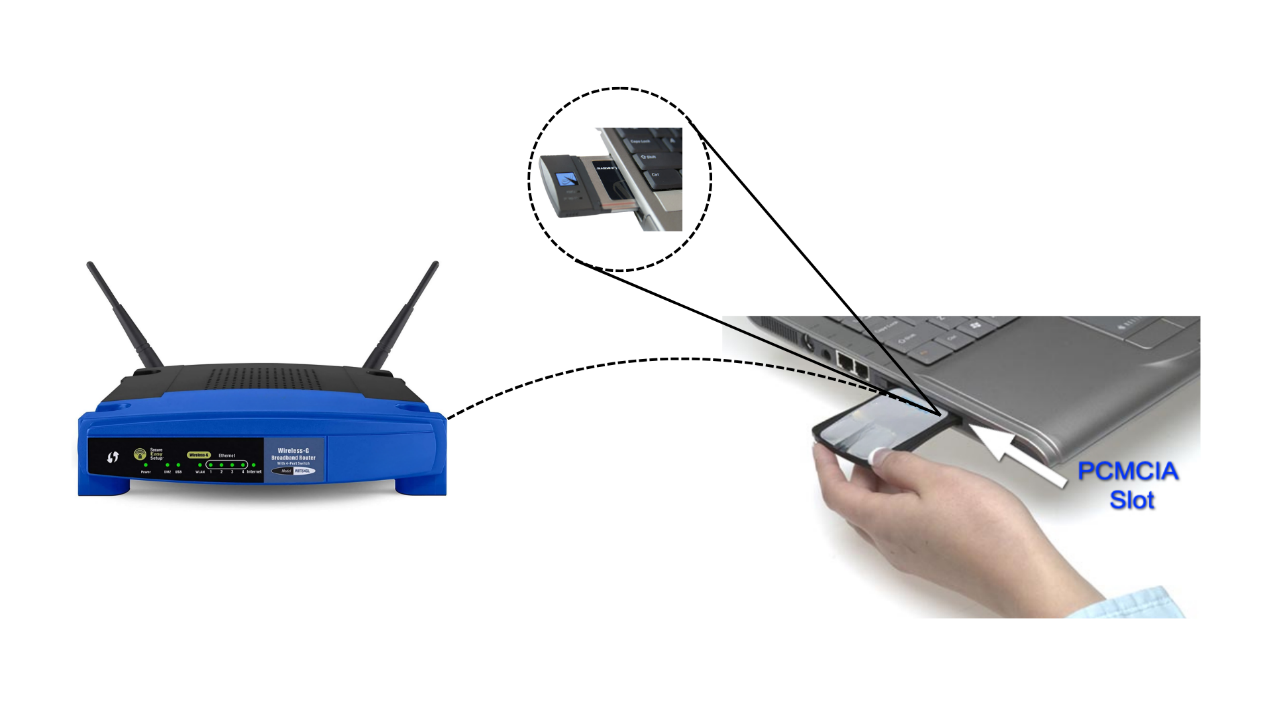
One of the most memorable moments in tech history happened in 1999, thanks to Apple's legendary co-founder, Steve Jobs. At a major Apple event, Jobs unveiled the brand new Apple iBook—the first widely available laptop with built-in Wi-Fi.
But it wasn't just the laptop's design that stunned the crowd—it was what Jobs did next. In a move that seemed almost like magic at the time, he picked up the iBook, disconnected it from all cables, and started walking across the stage. The audience watched in amazement as Jobs browsed the internet wirelessly, in real time, with no cords or cables. For most people, this was the first time they'd ever seen a computer online without being tethered to a desk and any external PCMCIA card.
This live demo didn't just show off a new Apple product—it showed the world what Wi-Fi could do. Suddenly, wireless internet felt real, possible, and within reach for everyday users. The crowd's enthusiastic reaction went viral, sparking headlines and conversations around the globe.
A New Era of Connectivity
After that moment, the world's relationship with the internet changed forever. Wi-Fi adoption skyrocketed:
-
Laptops became lighter, more portable, and standardly equipped with Wi-Fi.
-
In 2008, the arrival of smartphones—most notably the iPhone—put Wi-Fi in everyone's pocket.
-
By 2010, tablets brought Wi-Fi into new places: classrooms, coffee shops, airplanes, and even hospitals.
Wi-Fi moved from being a luxury to a necessity. It quickly became the heart of digital life, powering everything from video calls and streaming to smart home devices and cloud computing.
[Timeline showing laptops, smartphones, tablets, and smart home devices joining the Wi-Fi world.]
5. Wi-Fi in Home
Back in the early days, home Wi-Fi was a far cry from what we enjoy today. It was just fast enough to check your email or browse basic websites, streaming videos or making video calls was almost unthinkable.
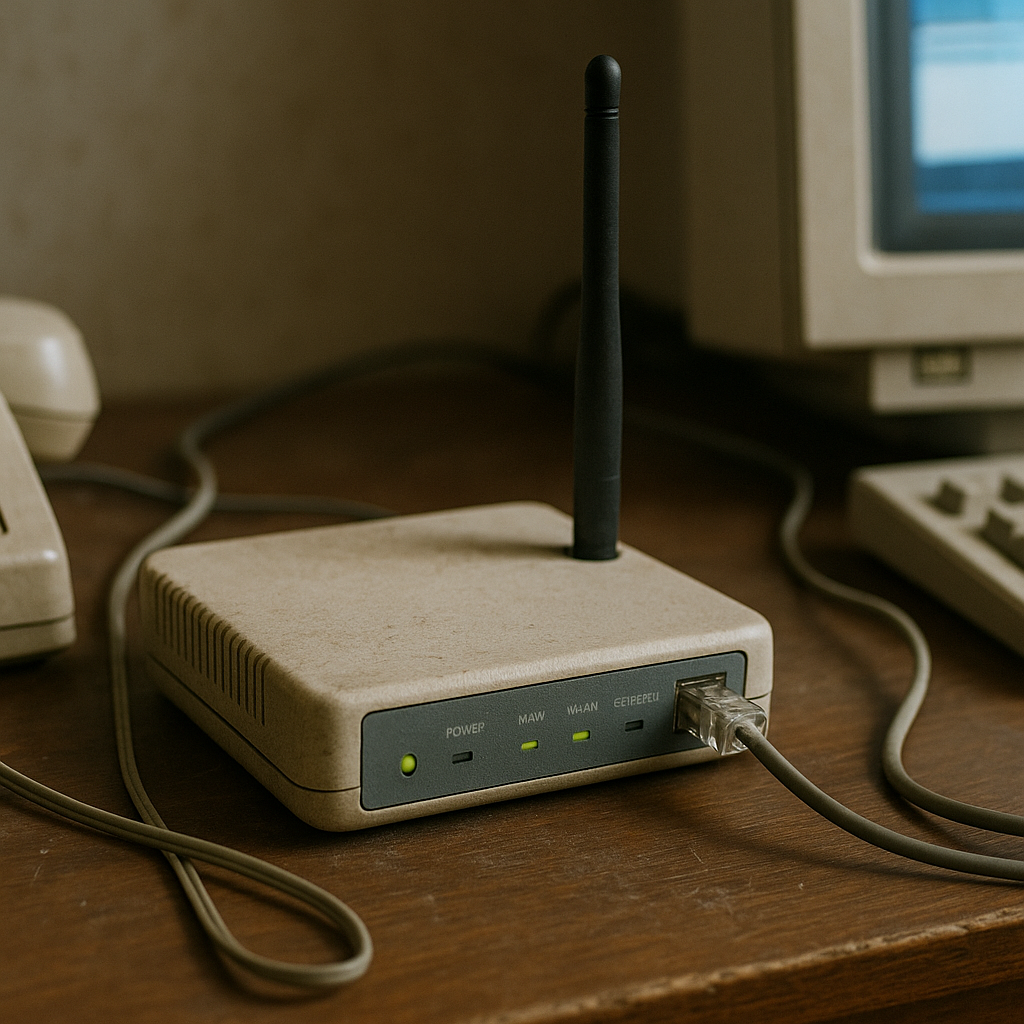

Most homes connected their Wi-Fi router to the internet through a dial-up or DSL phone line, and typical speeds were only a few megabits per second at best. Downloading a photo could take several minutes, and if someone picked up the phone, your connection might even drop!
Wi-Fi made things wireless, but the real "always-on, high-speed internet" experience was still years away.
Over time, Wi-Fi routers got not just faster, but much more affordable. What was once a tech luxury became a household staple. Internet service providers (ISPs) started making it even easier by bundling Wi-Fi routers together with cable TV and landline phone packages—one box for everything!
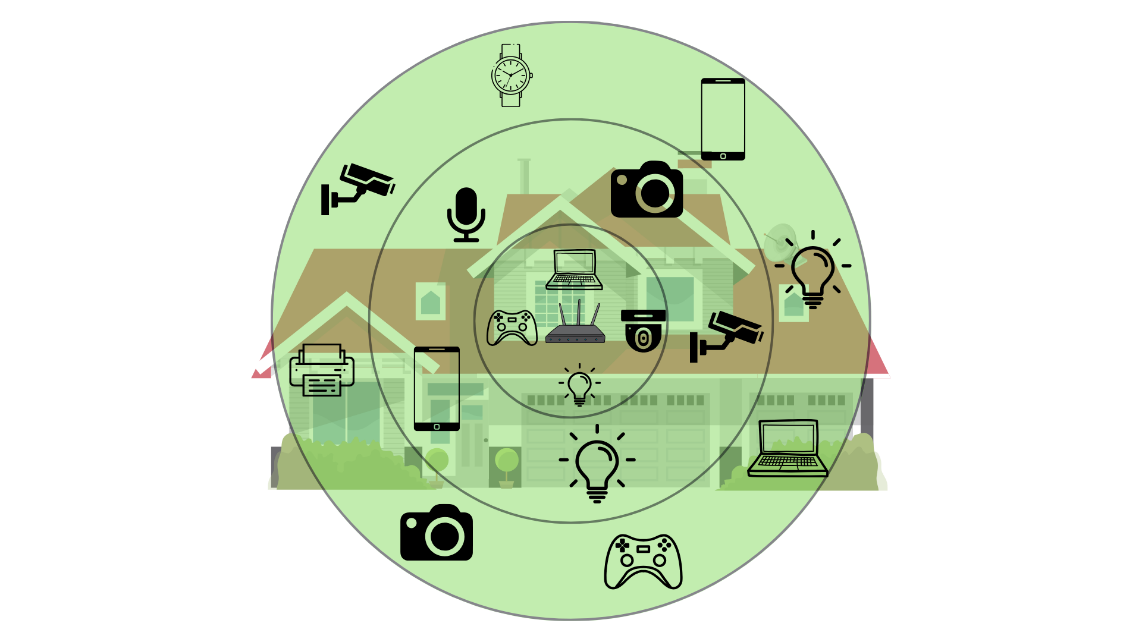
As technology advanced, our homes began to fill up with smart,
Wi-Fi-connected devices. It's no longer just laptops and
smartphones—now your TV, thermostat, security cameras, doorbell, and
even the refrigerator can connect to Wi-Fi. For many families, it's
common to have 20 or more devices all sharing the same home
network!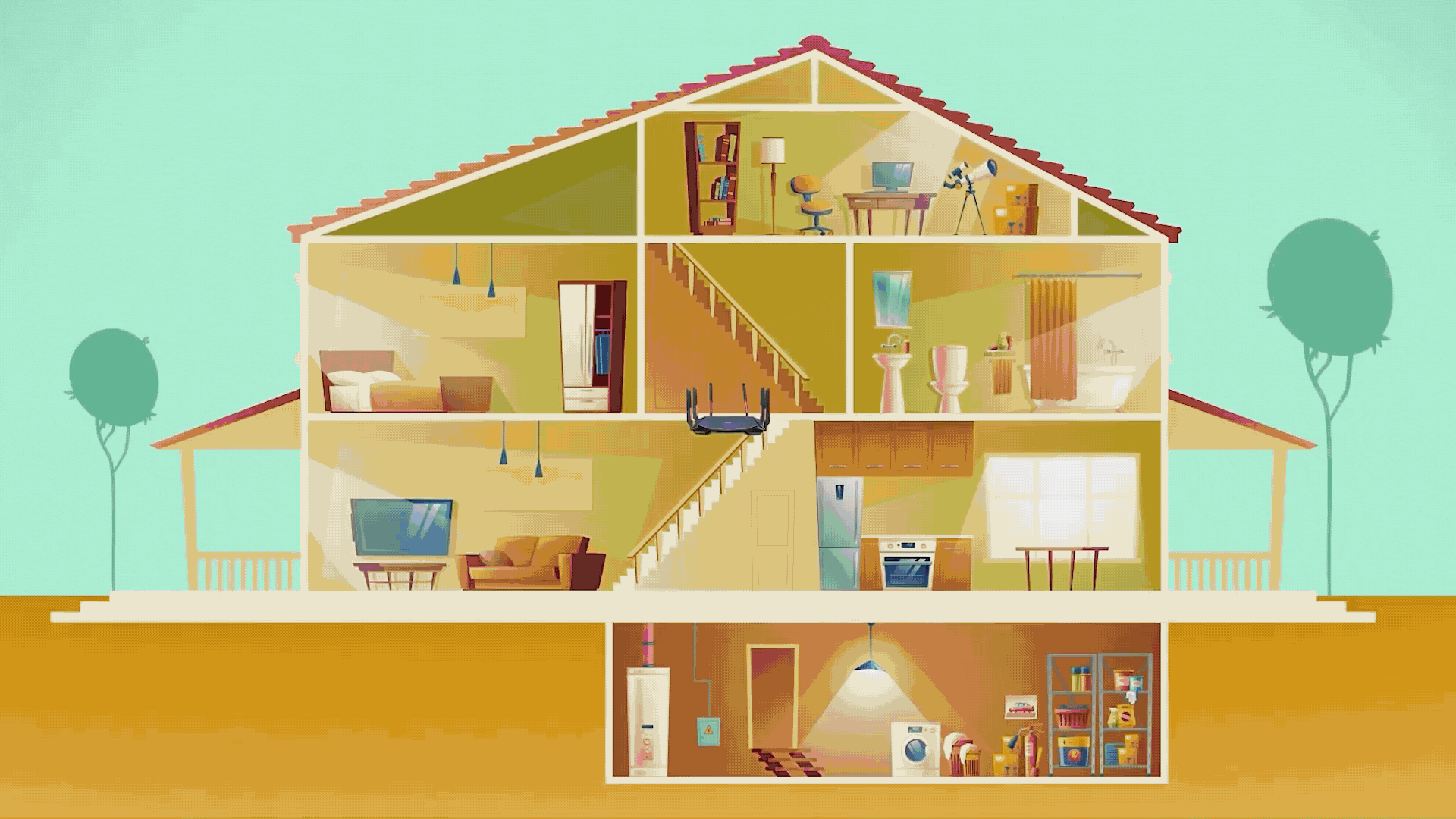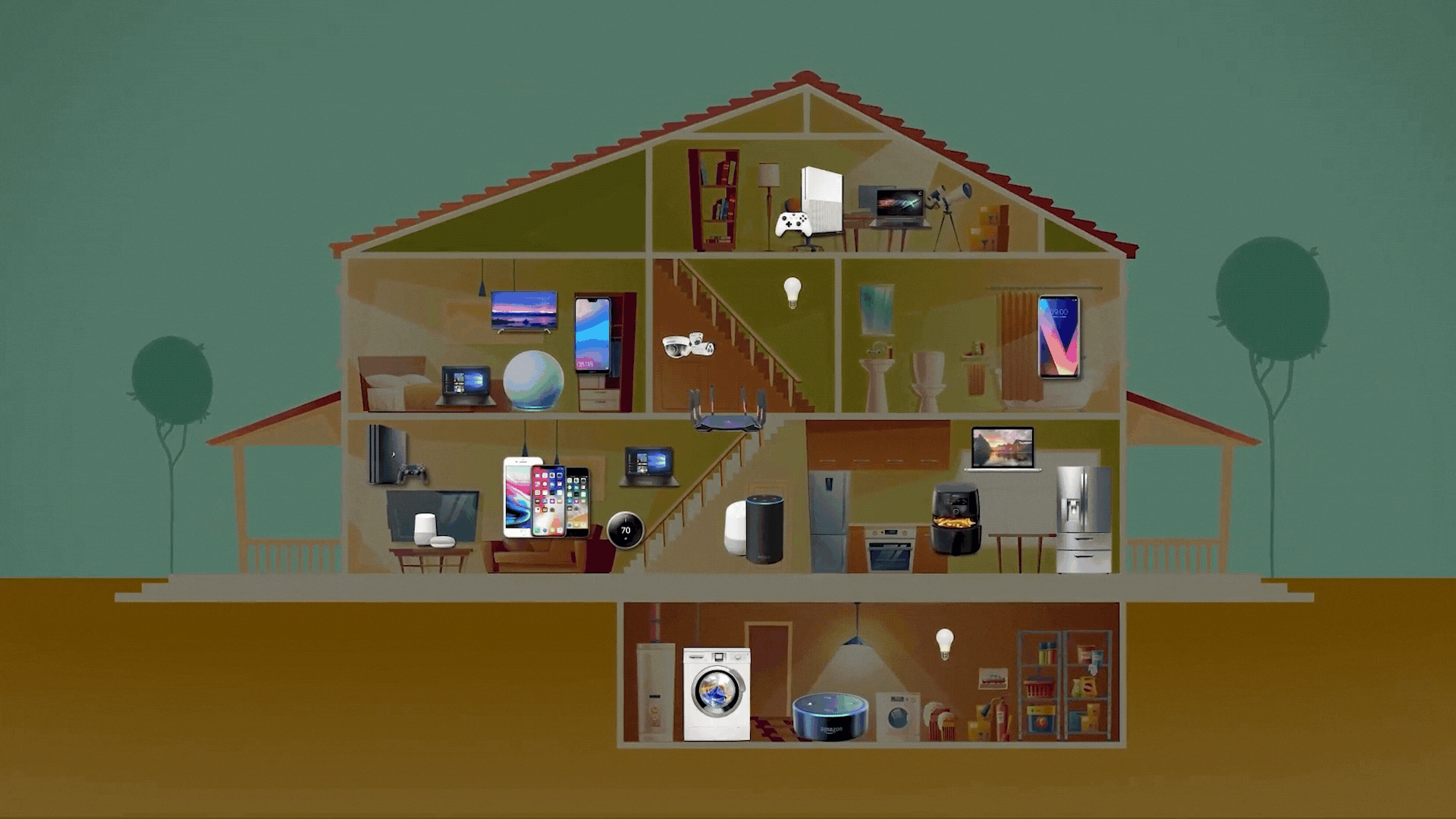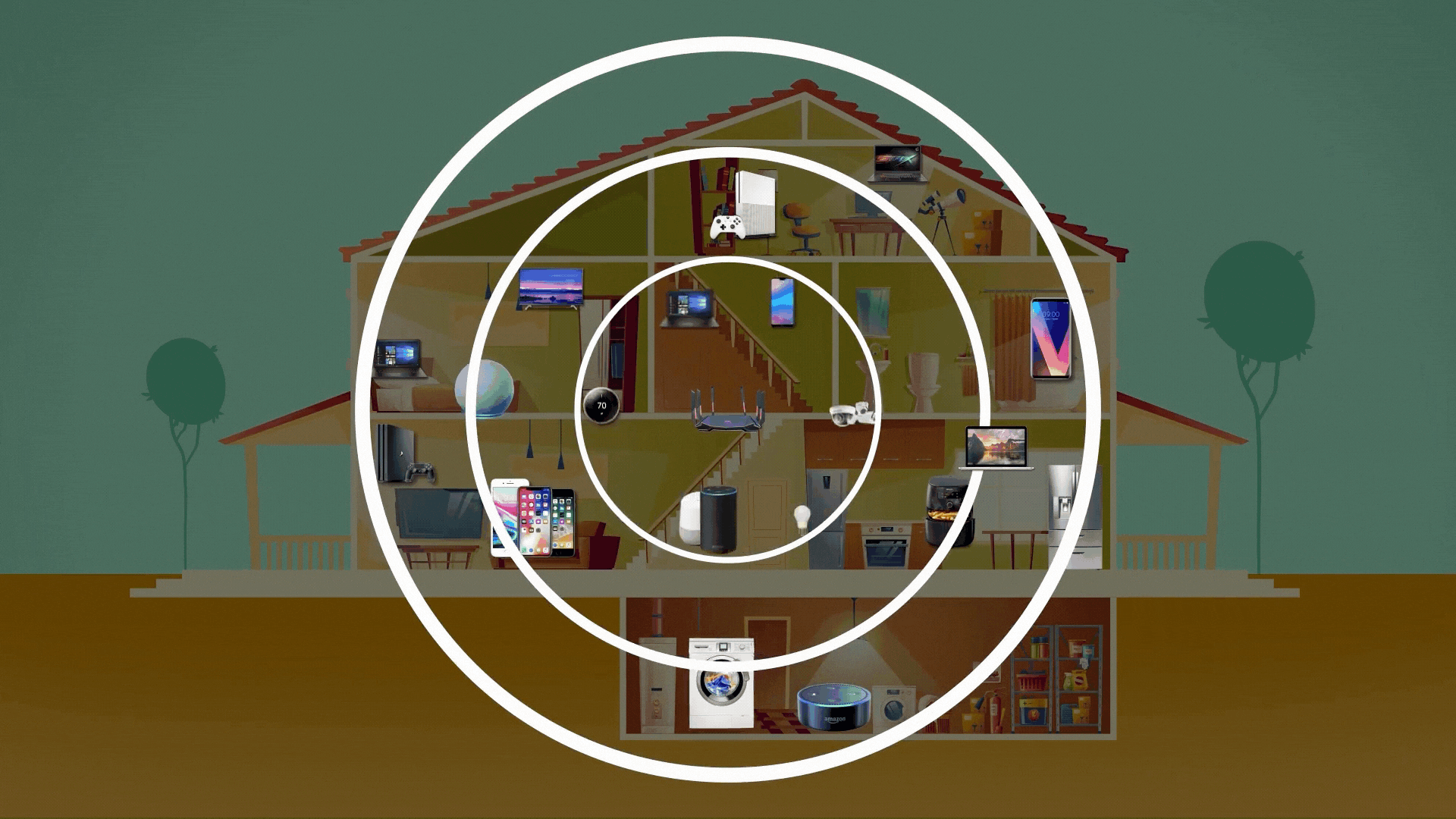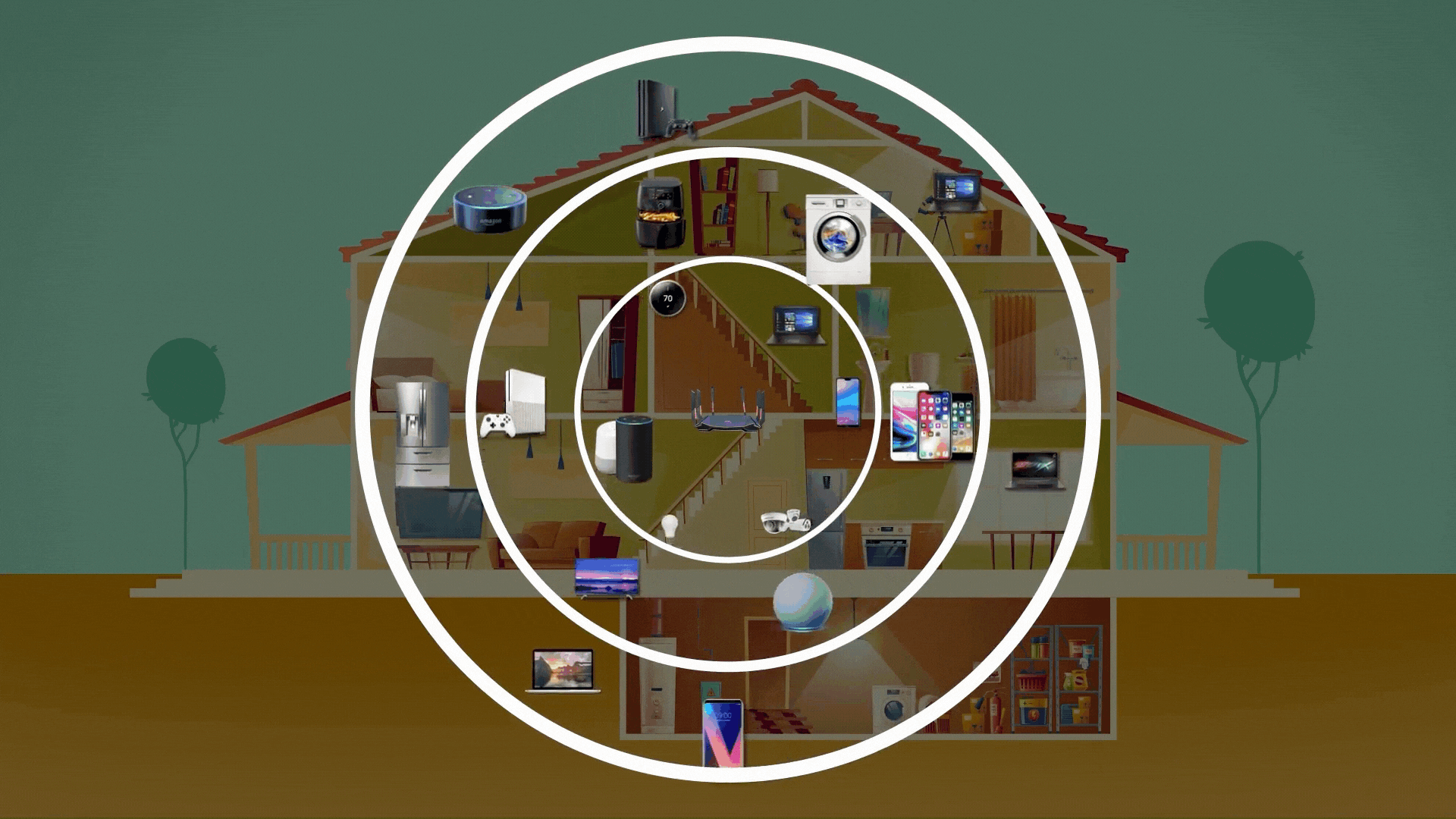
Mesh Networks
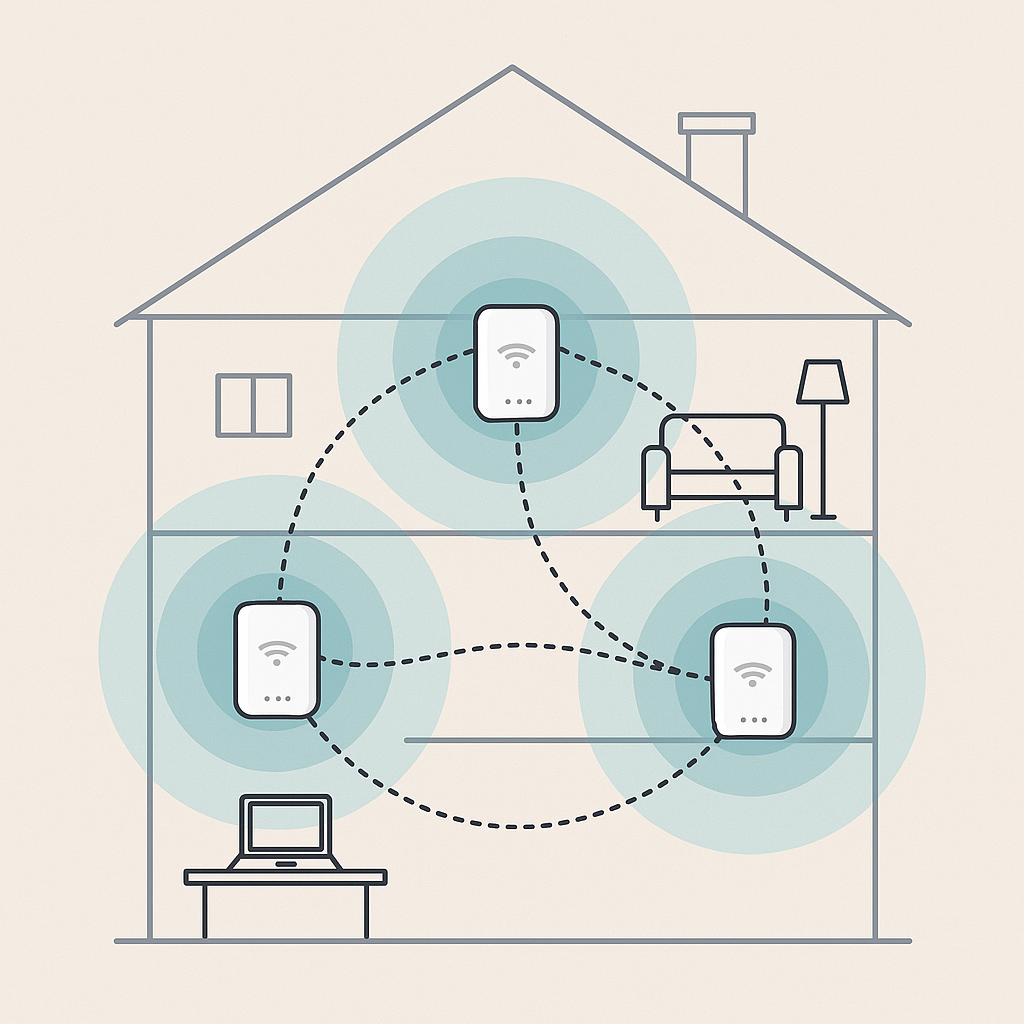
As homes became larger and our Wi-Fi needs grew, a single router wasn't always enough to reach every corner. That's where mesh Wi-Fi systems come in.
Instead of relying on just one router, mesh networks use multiple devices (called nodes or extenders) placed around your home. These nodes work together to create a seamless, strong Wi-Fi signal everywhere—from the living room to the backyard.
Mesh Wi-Fi keeps you connected wherever you are in the house: mesh focuses on eliminating dead zones and dropped connections in your house!
[Image: Diagram of a mesh network with multiple routers/extenders covering a home.]
6. Wi-Fi in Enterprise and Industry
Wi-Fi also changed the way offices, universities, stadiums, and
hospitals operate. Enterprises started with individual access points but
moved to centrally managed networks (controllers), and now cloud-based
management.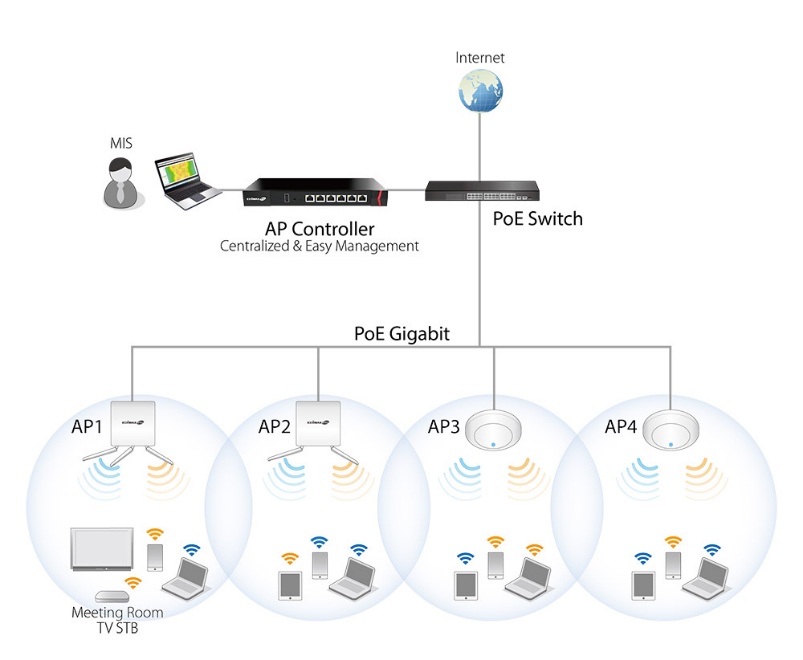
[Image: Diagram: Enterprise building with several Wi-Fi access points, all connecting to a central controller, then to the cloud.]
Today, artificial intelligence and machine learning help Wi-Fi networks "self-heal" and optimize themselves---making them easier to manage, even with hundreds of devices.
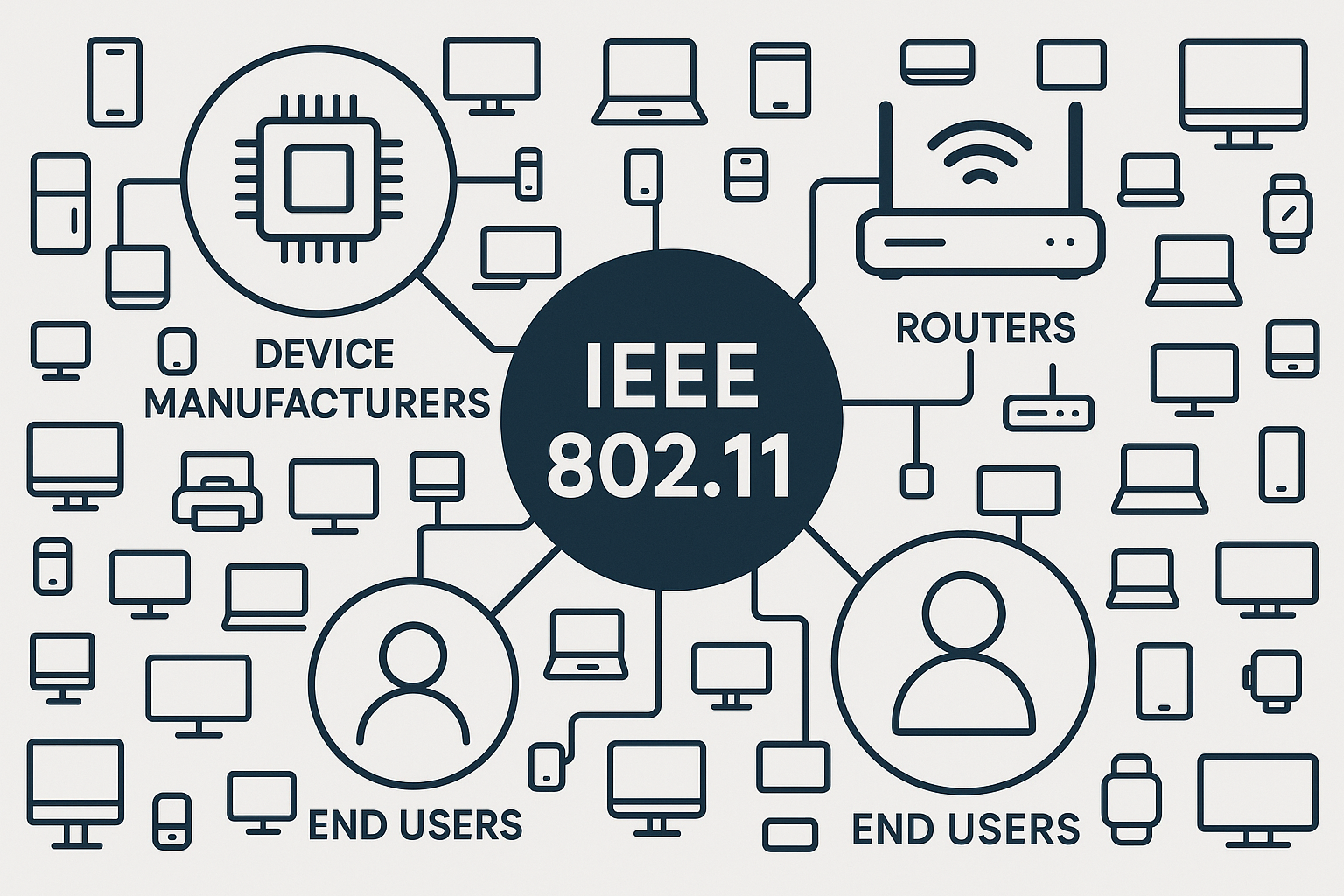
7. How Wi-Fi Devices Are Made: The Complete Wi-Fi Technology Life Cycle
Ever wondered how a Wi-Fi router gets from an idea to your home or office? The Wi-Fi technology life cycle is a step-by-step process that takes a business need, turns it into a global standard, designs and manufactures the necessary hardware, and finally delivers fast, reliable wireless internet to people all over the world. Here's how the Wi-Fi industry ecosystem works---explained in simple terms!
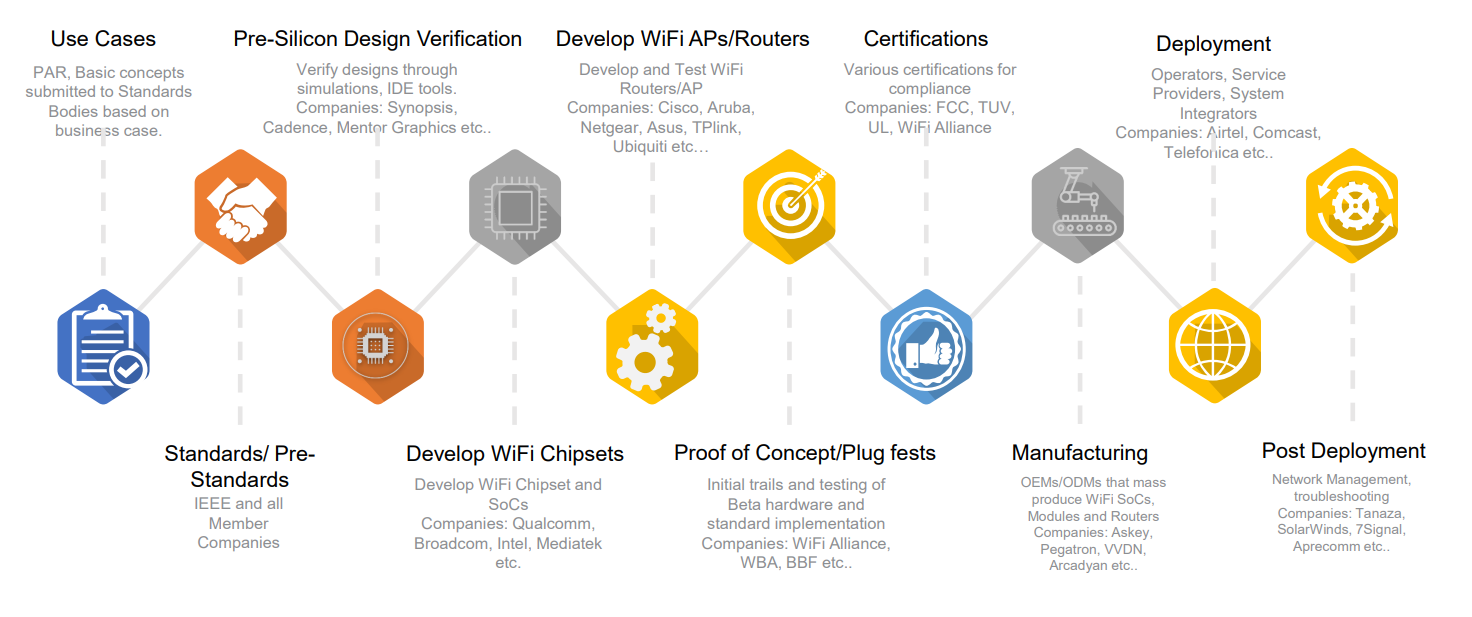
1. Identify Business Need / Use Case
Every Wi-Fi upgrade starts with a real-world problem or a new idea---like faster speeds or better security---that experts want to solve.
2. Standards Setting
Organizations like IEEE bring together companies to agree on new technical standards, making sure Wi-Fi works everywhere and for everyone.
3. Pre-Silicon Design Verification
Before building actual chips, engineers use powerful software to test and verify their designs through computer simulations.
4. Wi-Fi Chipset Development
Companies design and produce the tiny chips (SoCs) that make Wi-Fi possible in routers, smartphones, and countless other devices.
5. Router and Access Point Developments
Popular brands use these chipsets to build and test Wi-Fi routers and access points for homes, businesses, and public places.
6. Proof of Concept & Plugfests
Early versions of new Wi-Fi devices are tested in real-world settings to ensure they work well and can connect with other products.
7. Certification
Devices must pass strict certifications for safety, performance, and compatibility before they reach the market.
8. Mass Manufacturing
Once approved, manufacturers produce millions of Wi-Fi modules, routers, and chips for customers worldwide.
9. Deployment
Internet service providers and system integrators install Wi-Fi networks in homes, offices, schools, and public spaces.
10. Post-Deployment Management
After installation, networks are monitored and maintained for speed, coverage, and security—solving problems as they arise.
8. Why Is Wi-Fi So Successful?
If you ask why Is Wi-Fi Everywhere? The real reasons behind its popularity are:
-
Affordable: No need for expensive cellular towers or complex cabling---just a router and an internet connection.
-
Open and Flexible: Uses unlicensed frequencies, so anyone can set up Wi-Fi without big fees.
-
Works with Everything: Laptops, smartphones, printers, smart TVs, and even refrigerators.
-
Fast and Scalable: Wi-Fi speeds have grown from a few Mbps to multi-gigabit---enough for streaming, gaming, and more.
-
Secure: Improved encryption keeps your data safe.
In 2025, there are more than 27 billion Wi-Fi devices worldwide, almost three for every person on earth!
9. The Generations of Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi technology has evolved dramatically over the past two decades, with each generation introducing faster speeds, better coverage, and smarter features. The main Wi-Fi standards are created by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) and are identified as 802.11 followed by a letter or number (like 802.11n or 802.11ax). Over time, the Wi-Fi Alliance also started using easy-to-remember names: Wi-Fi 4, Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6, and so on.
A Quick Overview of Each Generation
-
Wi-Fi a/b/g (1999--2003): The first mainstream Wi-Fi standards (IEEE 802.11a, b, and g), made wireless networking possible in homes and offices. They allowed devices to connect without cables, offering new flexibility and convenience, and set the foundation for future Wi-Fi advancements.
-
Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n, 2009): The first generation to use multiple antennas (MIMO), offering much higher speeds and better reliability. Widely adopted in homes and businesses. Many developments such as Guard Intervals, Block ACKs etc. have been introduced in this standard boosting the speeds of the network.
-
Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac, 2014): Brought gigabit-level speeds into wireless networks, also had better performance in crowded areas because of lesser interference, and the channel bandwidth got doubled from the previous standard increasing the spectrum availability.
-
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax, 2019): Designed for our ultra-connected world, with even faster speeds, support for many devices at once, lower latency, and improved security. This standard also introduced 6GHz spectrum to the Wi-Fi world.
-
Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be, 2024+): The latest and most advanced standard, promising multi-gigabit speeds, ultra-low latency, wider channels, and improved performance for next-gen applications like AR/VR and smart homes.
Wi-Fi Generations Comparison Table
| Generation | IEEE Standard | Max Speed (theoretical) | Frequency Bands | Typical Range | Max Antennas | Main Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi 1 | 802.11a | 54 Mbps | 5 GHz | ~35 m | 1 | Early 5 GHz, less interference |
| Wi-Fi 2 | 802.11b | 11 Mbps | 2.4 GHz | ~35 m | 1 | First mainstream, good range, slow |
| Wi-Fi 3 | 802.11g | 54 Mbps | 2.4 GHz | ~38 m | 1 | Backward-compatible, faster than b |
| Wi-Fi 4 | 802.11n | 600 Mbps | 2.4 & 5 GHz | ~70 m | 4 | MIMO, dual-band, higher speed/range |
| Wi-Fi 5 | 802.11ac | 6.9 Gbps | 5 GHz | ~35 m | 8 | Gigabit speeds, beamforming, 5 GHz only |
| Wi-Fi 6 | 802.11ax | 9.6 Gbps | 2.4 & 5 GHz | ~70 m | 8 | OFDMA, MU-MIMO, Target Wake Time, WPA3 |
| Wi-Fi 7 | 802.11be | 46 Gbps + | 2.4 / 5 / 6 GHz | ~70 m | 16 | 320 MHz channels, Multi-Link Operation, 4K-QAM |
Summary
Wi-Fi has become the backbone of modern digital life. Its rapid evolution, flexibility, and affordability mean it's everywhere—from your smartphone to factory robots. In the next modules, we'll dive deeper into how Wi-Fi works, its technology, and how you can master it.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wi-Fi
What is Wi-Fi and how does it work?
Wi-Fi is a technology that lets devices connect to the internet wirelessly using radio waves, making networking easy and cable-free.
How can I make my Wi-Fi faster?
Place your router in a central spot, reduce interference, use the latest Wi-Fi standard, and limit the number of connected devices.
Is public Wi-Fi safe?
Use a VPN if possible and avoid accessing sensitive data on unsecured networks.
How many devices can we connect to Wi-Fi at once?
Modern Wi-Fi routers can support dozens of devices...some even up to 100+ in homes and 1000+ in enterprises.
